Category Archives: Motivation
Lessons from Training
I came across another interesting article on the BBC website today. It was temptingly titled Can you win at anything if you practise hard enough? It told the story of a young table-tennis coach from the UK, named Ben Larcombe, who attempted to take his lumpy and “unsporty” friend and turn him, over the course of a year, into a top competitive player. As part of the process of writing a book on the topic of training and improvement, the pair documented Sam Priestley’s transformation from a sort-of player to an impressively good one, at least to my eyes. You can watch the whole thing unfold before your eyes in this video. The article includes, however, a rather bubble-bursting comment from an English tennis coach and expert named Rory Scott:
“He is nowhere near the standard of the top under-11 player in the UK.”
So the BBC writer goes on to ask this question: “Why did the project fail?” What? Just because Sam didn’t meet his goal of getting into the top 250 table tennis players in the UK in one year of practicing every day, doesn’t mean it was a failure at all. It shows the potential for people to learn when they are persistent and work hard regularly with good strategies and feedback. The rest of the article goes on to explore exactly that potential, largely from a cultural viewpoint of different attitudes to natural ability and the need to persist versus instantaneous gratification.
I’ve been seeing similar sorts of studies a lot lately. The last few years have seen a plethora of books and talks on similar topics: how far does practice take you? You can read about Josh Kaufman’s attempt to learn something in 20 hours, or watch him tell about it at TED. Or you can read about Joshua Foer attempting to get better at memorizing things in his book, Moonwalking With Einstein. Or if you are really serious about the source of greatness, whether is comes from genes or training, try The Sports Gene by David Epstein. And don’t forget Doug Lemov’s Practice Perfect, a book which has a focus on learning teaching.
Practice, I’m convinced, is important. But so are attitudes to practice, and so is the kind of practice you do and the the kind of feedback you get. If we can get these right, our learners will learn better and faster, which will lead to other benefits. Practice is a touchy issue in language teaching, a field still trying to come to terms with the “drill and kill” of the audio-lingual approach. But intense, focused practice with constructive feedback and repeated opportunities to incorporate that feedback and improve is something very important to the learning process. It takes a lot of time, to be sure, maybe even 10,000 hours (though see Mr. Epstein’s book for a good discussion on amounts of time), but impressive results are possible. That is something I want my learners to understand and buy into.
Mr. Larcombe has a website with more detailed info about the process of teaching table tennis. He is also currently preparing a book.
Making EFL Matter Pt. 5: Prolepsis, Debate, and Benny Lewis
 As a young man, I was part of a legion of English teachers working in Japan. A large number of us “teachers” working day in and day out at language schools and colleges were actually travelers trying to save money for their next trek through Nepal or to live on a beach on Boracay or Koh Samui (very different in 1986) for as many months as possible before they had to work again. At least some of these people, in order to be able to stay in Japan and teach/work, pretended to be in the country for the purpose of studying something–flower arrangement, karate, or Japanese language, for example. One guy, ostensibly studying Japanese, dutifully went to the immigration office each year to renew his visa. And each time, he struggled greatly with the rudimentary questions the officer asked him in Japanese. At the end of the conversation, the immigration officer would kindly offer him encouragement because “Japanese was a hard language” to learn.
As a young man, I was part of a legion of English teachers working in Japan. A large number of us “teachers” working day in and day out at language schools and colleges were actually travelers trying to save money for their next trek through Nepal or to live on a beach on Boracay or Koh Samui (very different in 1986) for as many months as possible before they had to work again. At least some of these people, in order to be able to stay in Japan and teach/work, pretended to be in the country for the purpose of studying something–flower arrangement, karate, or Japanese language, for example. One guy, ostensibly studying Japanese, dutifully went to the immigration office each year to renew his visa. And each time, he struggled greatly with the rudimentary questions the officer asked him in Japanese. At the end of the conversation, the immigration officer would kindly offer him encouragement because “Japanese was a hard language” to learn.
That same sentiment–that you are just studying the language and can’t really use it yet–is still surprisingly common in many institutional programs for learners of many languages. I have often heard college students say that they want to go to the US “after my English is good enough.” The opposite of this “not yet” concept is prolepsis, “the representation or assumption of a future act as if presently existing or accomplished” (from Merriam-Webster). It is a lovely little term I came across in Walqui and van Lier (2010). They recommend treating students proleptically, “as if they already possess the abilities you are seeking to develop” (pg 84). In other words, throw them in at the deep end, and both support and expect their success. High school and college in Japan are perfect places for putting this approach into practice. Why? Because learners have already had somewhere between 4 and 10 previous years of of English exposure and learning. It’s time to stop pretending that they can’t use it. Right Benny?
People like Benny Lewis are not usually taken seriously in the TESOL world, but they should be. Watch the video and see how many things he gets right. Polyglots learn languages successfully, he says at one point, because they are motivated to “use it with people” and they go about doing so. That is some good sociocultural theory there. He also dismisses five of the barriers that people so often accept to explain their own lack of success with language learning, and addresses the growth mindset and time and resource management that he and his friends have found a way to make work for themselves. But what I find most amazing about Mr Lewis and others like him is that they are living examples of acting proleptically with language learning. They learn it, use it, love it, and repeat. They don’t stop to worry about whether they are “ready.” They don’t let things like having few resources around, or no interlocutors nearby, to interfere. They challenge themselves to learn what they can and then actively seek out opportunities to use that, monitoring their progress by continually testing it out. I admire their passion. I borrow strategies and techniques from them to pass on to my students. If we are not helping our students make use of Skype or Memrise or Quizlet or any of the many other tools available, we are doing a great disservice to our young charges.
But not only should we be introducing websites, we should be expecting our learners to use them and to push their learning. You can do it. No excuses. Of course you can handle basic conversations in the language. I expect nothing less than that. And let’s see what you can really do when you push yourself. I expect success. I assume it and design my activities around it. Prolepsis. We sometimes hear the word rigor used to describe education. We can also talk about holding higher expectations for our learners. Without a curriculum designed with the idea of prolepsis, however, it is likely empty talk. It sounds good, but is not actionable. Van Lier and Walqui list these three directives if we are serious about really making our curriculum, well, serious:
- Engage learners in tasks that provide high challenge and high support;
- engage students (and teacher) in the development of their own expertise;
- make criteria for quality work clear for all
We can see immediately that some of the things Mr. Lewis is suggesting get learners to do these things. I’ve talked before about rubrics and portfolios and making the criteria for success clear in other blog posts, but today I’d like to finish up this post by talking about an activity that does all these things, and it gets students to perform proleptically: debate. Now debate has a bad reputation in Japan. Many teachers think it is too difficult for students. Some teachers think it focuses too much on competition. These points may have some validity, but they should not prevent you from doing debate. We do debate, like JFK said we should go to the moon, because it is difficult. And if we have students debate both sides of issues, what begins to emerge is a keen sense of examining any issue–for looking at what is important and how important, and questioning and explaining that. Debaters behave proleptically, because they have to. Debating adds critical thinking structure to discussions about plans. Debaters learn to consider the status quo. They learn to evaluate plans in terms of their effect and importance. They learn to write speeches describing these things, and they learn to listen for them and consider them critically. Because there is a set structure, we can support and scaffold our learners. But we cannot hold their hands all the way. Debate forces them to go off scripts at times, while never going off topic. There is also time pressure, and the debate takes place with other people, an on-stage performance that is intimidating for everyone, and thus spurs learners to try harder. Yet, like scrimmaging with feedback, there are multiple opportunities to fine tune performance (and get repeated input). Every time I read about techniques to promote high standards, rigor, etc. , I always think to myself: That sounds an awful lot like debate, or Yup, debate can do that. To me, it seems that debate is one technique that should not be left out, especially policy debate where learners research topics to come up with arguments for both sides in advance. Not only do we get four-skills language development, but we also get research skills, organization skills, and critical thinking skills development.
Show me another activity that does that.
This post is part of a series considering ways to add more focus and learning to EFL classrooms by drawing on ideas and best practices from L1 classrooms.
Part 1 looked at the importance of goals. Part 2 looked at using data and feedback. Part 3 looked at the challenges and benefits of academic discussions Part 4 looked at portfolios and assessment
Making EFL Matter Pt. 4: Portfolios and Assessment
In principle, a portfolio is an easy to understand and intuitively attractive concept: students keep the work they produce. The real challenge of a portfolio is what you do with it. Without a clear vision of how the tool will be used, it can easily end up being a little like a child’s art box of works produced in art class in school over the years—just a repository of things we hold on to for no specific reason other than sentimental attachment. We might pull these works out to look at them from time to time, but they are not a clear record of achievement, nor can they help inform future learning decisions. The central function of a quality portfolio is to clearly provide evidence of growth and to “…engage students in assessing their growth and learning” (Berger, Rugen & Woodfin, 2014, pg. 261). Specifically what growth depends on the goals of the course or program. When a course or program has clear goals, a portfolio can have a formative or summative role in demonstrating a learner’s achievement or progress toward achieving those goals. There are also practical/logistical constraints on portfolio deployment. What artifacts should be included, how many should be included, where should the artifacts be stored, and how will the portfolio be assessed and by whom, are all important decisions. The results of these decisions can greatly impact the success of a portfolio as a learning tool.
Conceptualizing a portfolio
A portfolio is not simply a repository file. It must serve as a record of progress that is used to assess learning by the learner him/herself or by others. All decisions on its structure and deployment must start with this basic understanding. The design of the portfolio itself, and its integration into the syllabus (i.e., how it will be used on a regular basis) must aim to make it as easy as possible to record progress/achievement, to make visible evidence or patterns progress/achievement in the collected data. For this reason, not only student-produced academic work (essays, presentations, tests), but also documents that make progress and achievement salient should be kept in a portfolio. Such documents may include introductory statements, target-setting plans, records of times on tasks, assignment rubrics, progress charts, and reflection reports.
The importance of goals
In order to be effective, the portfolio must be closely aligned to the goals of the course or program and be able to show progress toward or achievement of those goals. In other words, it must be able to provide specific evidence of progress in achieving the target competencies in a way that is clear and actionable. It must also do so in a way that makes the most effective or efficient use of time. These goals can include knowledge goals, skill goals, or learning goals for constructs such as responsibility, autonomy, revision, collaboration, service and stewardship (to name a few). Without clear goals (usually arranged in a clear sequence), effective use of a portfolio cannot be possible. Without clear goals, the formative and reflective functions of a portfolio cannot be leveraged in a clear and actionable way. However, if students know what they are aiming for and can compare their work in how it meets the target competencies (using the descriptions and rubrics that define the goals/competencies), portfolios can be a powerful tool for reflection and formative feedback.
The importance of regular portfolio conversations
“In order for portfolios to be a tool for student-engaged assessment, including formative and summative assessments, they must be a regular part of the classroom conversation, not a static collection of student work” (Berger, Rugen & Woodfin, 2014, pg. 268). The portfolio must be a tool of measurement, like a bathroom scale, and can only be effective if it is used regularly. Students must regularly enter data into it (more on what kinds of data in the next section), and they must use it to look for patterns of success and gaps in learning/performance and strategy use. For this reason, providing clear guidelines and time to enter data into portfolios, facilitating the noticing of patterns and gaps, and giving opportunities for students to discuss their progress in groups, are all necessary. This will require classroom time, but also some scaffolding so students can understand how to work with data. Student-led conferences (mini presentations on progress done in groups in class) can be a useful tool. In groups, students can practice talking about learning, but also compare their progress and efforts with those of their classmates. Counselor conferences can also make use of portfolios, and if students have practiced beforehand in groups, time with counselors can be economized. Finally, to truly leverage the power of portfolios, passage presentations (public presentations where students explain and defend their learning accomplishments to groups of teachers, parents, or other concerned parties) can be particularly powerful since they are public and official. If a passage presentation system is in place, it will serve to make the portfolios more meaningful, greatly enhancing the effort students will put into entering and analyzing data and the amount of time they spend analyzing and practicing explaining their learning. Passage presentations and counselor conferences can transform student-led conferences into the role of practice for “the big games.”
Portfolio contents Pt. 1: What are we trying to develop?
Let us review our key points so far. It must be easy to enter meaningful data into the portfolio and notice trends or gaps. Noticing the trends and gaps in performance requires an understanding of the goals of the course/program, so they must be clear. The portfolio should be used regularly: students should use it to monitor their learning; and students should be able to refer to it when explaining their learning to others (groups, counselors, or others). These points are all concerned with usability, making the experience of using a portfolio as simple and smooth and effective as possible. What we actually put into the portfolio must be concerned with our learning targets. As mentioned earlier, any program or course will have multiple targets for knowledge and skill acquisition, but also for constructs such as digital literacy, critical thinking, problem solving, responsibility, autonomy, revision, collaboration, service and stewardship, and possibly others. Therefore, it is important for portfolios to contain finished work and evidence of the process of improving work through working with others, checking and revising work responsibly, and helping others to do so, too. Portfolios should also contain records of learning activities and times on tasks as evidence of autonomy and tenacity.
Portfolio contents Pt. 2: Portfolios for language learners
As part of English language courses, there are usually weekly classroom assignments for writing and presentation. There may also be other writing assignments, or other speaking assignments. As for other constructs, the following have been shown to be important for successful language learning and therefore should be part of the curriculum:
- Time on task
- Time management (efficient use of time)
- Commitment to improvement/quality (accountable for learning)
- Critical evaluation of learning strategies
- Collaboration (accountable to others)
- Seeking feedback and incorporating feedback (revision)
If we try to build these into our portfolio system along with our language and culture target competencies while still managing the volume of the content, I believe that we must include the following elements, in addition to a general goal statement:
- Drafts and final products for a limited number of assignments, including a reflection sheet with information about the goals of the assignment (and a copy of the rubric for the assignment), time spent on the assignment, attempts at getting feedback and comments on how that feedback was included;
- Weekly reflection sheets (including a schedule planner) in which students can plan out the study plan for their week before it happens, and then reflect upon the results afterward. There could also be sections where students can reflect upon strategy use and explain their attempts to reach certain goals;
- Self-access tracking charts in which students list up the reading, listening, or other self-access activities students engage in. Several of these charts can be made available to students (extensive reading charts, extensive listening charts, TOEFl/TOEIC test training, online conversation time, etc.) and students can include the charts relevant to their personal goals (though extensive reading will be required for all students).
Finally
As you can see, there is much to be decided: specifically which assignments and how many will be included; also the various forms need to be designed and created; and, for the English classes, whether completing the portfolio and discussing learning is something that we want to scaffold learners to be able to do (something that I personally think is very important).
This post is part of a series considering ways to add more focus and learning to EFL classrooms by drawing on ideas and best practices from L1 classrooms.
Part 1 looked at the importance of goals.
Part 2 looked at using data and feedback.
Part 3 looked at the challenges and benefits of academic discussions
References
Berger, R. Rugen, L., and Woodfin, L. (2014). Leaders of their own learning: transforming schools through student-engaged assessment. San Fransisco: Jossey-Bass.
Greenstein, L. (2012). Assessing 21st century skills: a guide to evaluating mastery and authentic learning. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
Language on Stage: Debate and Musicals
In his 2011 book Creative Thinkering, Michael Michalko explains the idea of conceptual blending. What you do is take dissimilar objects or subjects and then blend them–that is, force a conceptual connection between them by comparing and contrasting features. It’s an enlightening little mental activity that can help you to come up with creative ideas or insights as you think about how the features of one thing could possibly be manifested in another. In the past few days, I’ve tried blending two activities that I’ve seen push EFL improvement more than any other: performance in club-produced musicals, and competitive policy debating. I’ve compared them with each other and with regular classroom settings,
I chose these two because over the last few years I have seen drama and debate produce language improvements that go off the charts. This improvement can be explained partly in terms of the hours on task that both of these activities require and the fact that students elect to take part voluntarily, but I don’t think that explains everything. There are certainly other possible factors: both require playing roles; both are team activities; both have performance pressure; both reward accomplishment; both require multi-modal language use and genre transformation; both require attention to meaning and form; both are complex skills that require repeated, intensive practice to achieve, and that practice is strictly monitored by everyone involved, who then give repeated formative feedback. Not complete, but not a bad list, I thought.
But then while reading Leaders of Their Own Learning, a wonderful sort of new book by Ron Berger, Leah Rugen, and Libby Woodfin, I came across this quote by a principal of a middle school in the US:
“Anytime you make the work public, set the bar high, and are transparent about the steps to make a high-quality product, kids will deliver.”
I think the speaker hit the nail on the head as to why activities like debate and drama work: public, high expectations, and clear steps. Aha: public! The dominant feature of debate and drama is that there is a public performance element to them. Students prepare, keenly aware that they will be onstage at some point; they will be in the spotlight and they will be evaluated. Of course students need support and scaffolding and lots of practice before they can get on stage, but unless there is a stage, everything else won’t matter as much. It is the driver of drivers. Is that pressure this message suggests? Yup, but also purpose. I have seen kids transformed by the experiences of competitive debating or performing in a musical. I refuse to believe that the mediocrity I see in so many language course and programs is the way it has to be.
So, to get back to the whole reason for this little thought experiment: how can we take these best features of debate and drama and apply them to language programs? The key, I hope you will agree, is introducing a public performance element. There needs to be some kind of public element that encompasses a broad range of knowledge, skills, and micro-skills, and then there needs to be sufficient teaching, scaffolding, and practice to ensure public success. But how…?
Over the next few blog posts, I’ll be exploring these issues, drawing from ideas that are being developed in K-12 education in the US, particularly in approaches that have been working in high-challenge schools with English language learners and other at-risk learners (for example, by Expeditionary Learning, WestEd, and Uncommon Schools). In particular, I’ll be looking at ideas in Leaders of Their Own Learning (mentioned and linked above), Scaffolding the Academic Success of English Language Learners, by Walqui and Van Lier, and the soon-to-be-released second edition of Teach Like a Champion 2.0 by Doug Lemov. I’ll be looking at all of these through the lens of an EFL teacher in Japan. Many things in these books won’t be applicable in my context, but I suspect many may help inform ways of improvement here.
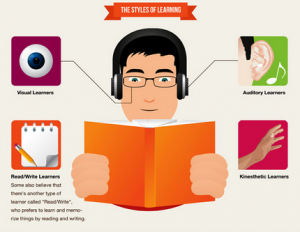
Learning Styles
One idea that comes up again and again is that of learning styles. Of course you have heard about it: some people are visual learners, some people have to hear things to learn them, and some kinesthetic people need to get their whole body into the learning process or nothing sticks. Google these terms–visual, auditory, and kinesthetic–and you’ll get enough hits to make you think that learning styles constitute an established theory in learning.
Unfortunately, that assurance would be misplaced. Daniel Willingham, in When Can You Trust the Experts?, has this to say:
…there is no support for the learning styles idea. Not for visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learners…The main cost of learning styles seems to be wasted time and money, and some worry on the part of teachers who feel they ought to be paying more attention to [them]…(page 13).
This comes as quite a shock for many people because the idea is so entrenched. “Experts” talk about it often. It is mentioned in countless books and articles. I have heard it many times and repeated it myself. But, nope, it just ain’t so. There is no such thing as a “visual learner.” At least, there is no demonstrated effect in any scientific study. Mariele Hardiman summarizes the myth and the reality nicely in The Brain-Targeted Teaching Model. She cites Pashler et al. (2008), where you can read it yourself if you are still numb in disbelief (citation below). Hattie and Yates have a unit devoted to this myth if you are still not convinced. Great book, by the way.
But your intuition tells you that there are differences between learners. There most certainly are. Every brain is wired differently because of the individual’s experience and their age of development (for children). These developmental differences and experience differences are real and have very real consequences for how we should teach and the best sizes for classes, if we take differences seriously.
Essentially, differences take the form of preferences, preparation, motivation, and pace. According to David Andrews of Johns Hopkins University in the wonderful MOOC named University Teaching 101, students have preferences for the modality (yes, here we can talk about print or video or audio), groupings, and types of assessment and feedback. Students also vary in how prepared they are to learn. All learning involves connecting new knowledge to knowledge already held. If your students lack certain schema or factual knowledge, they will need more time to gain that and the target knowledge. In any given class, motivation differences (often because of prior experience) and time commitments can produce huge differences in the amount of attention and effort students will exert and sustain. Lastly, processing speeds (again because of experience and practice) in reading and auditory processing can make content more or less challenging than the instructor may think it is. Watch any class taking a test to see pacing differences in action. Students finish at very different times, and this is often unrelated to proficiency with the target content.
So, what should an EFL teacher do? Well, smaller classes are a start, but only if you are really planning to do something about it. If you are going to teach to the same middle as always, smaller classes will not necessarily give your students any benefits. Small groupings ranks only #52 in Hattie’s list of effective interventions, probably for this reason. Mr. Andrews suggests personalizing content and delivery as much as possible. He suggests getting to know your students as much as possible, and giving them as much choice as possible in how they learn. This is a delicate balancing act, in my experience. Students can be notoriously bad at understanding themselves, their strengths and weakness, and choosing better strategies. The teacher must push and pull them carefully up to better performance, offering them choices and checking that they are choosing wisely and making sufficient effort to see results. Technology can help a lot here. Recording short lectures/lessons and making them available with transcripts to students can allow slower/less-experienced/different-preference students options for learning and reviewing that can allow them to customize the education experience for themselves. And research has shown that repeated viewing/reading and multi-modal presentation are significantly correlated with better learning; and variety and choice will keep attention better and improve motivation. One crucial part of personalization is personalizing formative feedback (a series of posts on formative assessment starts here). The power of formative feedback in driving learning should not be underestimated, but you need to be close to your students to either do that yourself or teach them or their classmates to do it. This also involves making goals salient to students with clear rubrics, so that they can see where they are going and how they are progressing, and what they need to do to get better. A recent study in math classes at an American university illustrates this. For homework assignments, some students were given formative feedback and follow-up problems based on performance, while the spacing of content repetition was controlled for maximum effectiveness. This small change resulted in a 7% improvement on the short answer section of the final exams! Personalization seems to have that kind of power, if done right.
As Mr. Andrews says, “personalization has become a standard for learning in every part of our lives except school. And it will become a standard in school.” Get ready to hear more and more about it.
Pashler, H., McDaniel, M., Roher, D., & Bjork, R. (2008). Learning styles: Concepts and evidence. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 9(3), 109-115.
Learning styles image fragment from https://www.home-school.com/news/discover-your-learning-style.php
Fine-tuning Your Classroom Skills: Doug Lemov Catalogs How to Teach Like a Champion
Hey! EFL teachers in Japan! No disrespect, but you probably need this book. If you are a native speaker EFL teacher in a country where there is more interest than accomplishment in learning English, you probably need this book. You might be one of the few educated, trained, and disciplined among us, but chances are, you are not. More likely, you belong to the majority– by and large and by most accounts, a ragtag bunch of misfits. Most of us fell into this profession and were not trained as teachers exactly; I mean, not in the sense of teachers who went to teachers college, studied theory and techniques, did practicums, and got jobs in school systems run by school boards, with standards, supervisors, paperwork, and training. Many of us were waiters, travelers, English majors, or other such mostly unemployables who began teaching EFL and then learned how to do it in a combination of certificate courses, graduate courses, conferences, and keeping our eyes open on the job. Or you may be a Japanese teacher of English as a foreign language, teaching in senior or junior high school after gaining a license that required only a few extra undergraduate courses, completion of a two or three-week placement at your old school, and passing the tests for the prefecture you are now employed by. You know your basic grammar, have a fairly good vocabulary, and are pretty confident that with a little prep time can explain anything between the covers of a textbook. But you have gaps in your knowledge of English usage and classroom management almost as impressive as the unwarranted overconfidence your native English-speaking colleagues bring with them into your school, so full or self-righteousness and irresponsibility. Both you groups of teachers would benefit from this book because not only were you never trained specifically for classroom and learning management, a lot has been learned about teaching and managing classes since you were at school. There is now a good mass of knowledge and techniques that I bet you never took a course in and most likely are unaware of.
This book is not aimed at EFL teachers, not even a little. But it will tell you, and show you, how to do things with your students that will get them to pay more attention, learn more deeply, and make the most of the time you are now probably doing a good job of frittering largely away. This book by itself will not solve your problems, and you’ll likely find it pushes more regimentation and rigor than either you or your students need, but man ‘o man there is a lot to be learned here. 49 techniques, roughly half of which you can adapt very nicely for an EFL classroom, are presented by Mr. Lemov. He gleaned them from observing teachers who were getting better-than-expected results in schools whose demographics made those results look almost miraculous. These are techniques that took chunks of a doomed demographic and put them on the Path to College. Some of them are techniques you might indeed be using. But I have managed enough native-English speaking teachers and observed enough Japanese teachers of English in high schools that I can say with quite a bit of certainty, you (and your students!) will benefit from this book. Mr. Lemov provides us with clear explanations, warnings against pitfalls, and short illustrative video clips to make the points easy to understand. Putting them to use will be more difficult, but not impossible, as most of the techniques require only slight adjustments in timing or language. But it is those small changes that can make a huge difference. Techniques such as Cold Calling (picking the student after you have asked the question), Pepper (asking a rapid sequence of questions as review), and concepts such as Ratio (getting students to do more of the thinking) and At Bats (maximizing practice opportunities) can transform the one-way slog of some English classes or the whimsical frivolity of others into real learning environments.
The book has a website. Go there first and look around. http://teachlikeachampion.com/ Learn a little about Uncommon Schools or Mr. Lemov himself and what he does. Watch some of the videos and see the control and confidence and learning on display. I am quite certain you will begin to see where you may be falling short now. These are schools and teachers who refused to let demographics get in the way of success, who challenge their learners to perform at a higher level, and demand their attention and effort. If you don’t know how to get to that point with your learners, then you probably need this book. It is not a panacea, however, and you will still need to adapt the ideas to fit your subject and classes. In general, the techniques are very cognitive and very behaviorist and so Japanese teachers of English will likely find them more immediately appealing as they will mesh more nicely with current practices. Teachers would do well to not forget the affective and emotional when planning lessons, something Mr. Lemov spends too little time on (from a language teacher’s perspective). But this book can give you a lot of help learning and improving techniques you probably were never exposed to in your education and your own training. It can help you make whatever you are doing more efficient and more effective.
EFL Gamification 5: The Whole Hog?

This is the fifth post on gamification in EFL. The first was an attempt to understand motivation. The second considered changing specific behaviors. The third looked at mechanics, or the structure needed to make game-based learning engaging. The fourth was about some of the problems that can happen when gamification (especially just pointsification–the casual addition of points and other game elements) is put to use for manipulative purposes without enough attention to the underlying motivations and personalities of learners. This post will look at turning your whole class into a game, or put more metaphorically, going the whole hog. There are really two ways of doing this. One is to design the course as a simulation. That means to create an immersive and realistic environment that requires learners to play a role. It is a kind of extreme content-based form of learning and requires considerable flexibility with curriculum content and probably works best if you are aiming learners at a specific career. An example might be simulating planning and opening a store for business students. The instructor would then need to create all the websites, documents, etc. needed to support the simulation. The second, and the one I’ll focus on in this post, involves re-imagining the present content using a role-playing game structure. Traditional content (including textbooks and teaching modules) are used, but a wider variety of tasks and assignments are used. Game genre details and a narrative structure are employed to make the progression through the material seem more like a game. This is more possible in institutional EFL courses, but still comes with a few conditions, the first being your familiarity with the genre of games.
Are you a gamer? I’m not talking about a little Angry Birds while commuting. I mean, have you spent huge blocks of your life immersed in World of Warcraft or Halo or The Sims or one of the many other places/pastimes where gamers spend time? Ask yourself how much you know about games and how much you really play. If you play 13 hours a week, you can consider yourself only an average member of the gamer sector of society; if you are up to 20 hours a week, you are officially “hard-core”; and if you can somehow cut your working, sleeping, and social hours down far enough to manage 45 hours a week, you are (by any account) “extreme” (McGonigal, 2011, p. 3). Of course, you don’t need to be a fanatic about games to turn your classroom into a game, but you do need a certain amount of familiarity with the genre. You will need rather intimate knowledge of the structure and pacing of games–the way items are acquired, the way quests go down, the types of challenges, the way characters interact, the reward systems, etc.–and you will need to be able to retool your classroom and syllabus in a way that mimics this. You will need to know the lingo: guilds, raids, wipes, (point) farming, experience points (XP), etc. Unsure of yourself? Back away from this idea now. But if you are a gamer and game lover, it is an option to embrace whole hoggedly. I speak as a researcher/observer here. I have not done this myself and so I will be only reporting on what I have read, pointing you to other sources and egging you to go out there and give it your best shot if you are interested.
There is, admittedly, something of a square peg in a round hole fit when taking the immersive multimedia world of a game and using it for a brick ‘n mortar face-to-face classroom. First of all, students are not sitting at computers interacting with audio/visual/narratives made by teams of talented professionals with an average production cost of $10 million (Whitton, 2010, in Using Games to Enhance Learning and Teaching). But if everyone is up for a bit of pretending, or suspension of disbelief, it can go well. Both Jane McGonigal in Reality is Broken, and Lee Sheldon in The Multiplayer Classroom believe that game culture is second nature for the students in our classes. They have grown up playing games and are very comfortable with the way games engineer player progression. Ms. McGonigal states that the members of the gamer generation have more problems with reality–including most school work–because it lacks interesting challenge, the satisfying work, promise of success, and actionable feedback that is usually the norm. In other words, most courses aren’t engaging for many learners and they are likely to be up for a change. Or as Mr. Sheldon optimistically puts it, “we have yet to discover a class that cannot be taught in this way” [as a game] (pg. 9).
Mr. Sheldon’s book is the best resource I’ve been able to find for designing coursework as a game. Indeed, that is the sub-title of the book. In addition to being a trial-and-error account of his attempts to do this with his own university game design courses, the book contains several case studies by different teachers, the closest one among them to a high school language course was Denishia Buchanan’s high school biology class. If you really have no idea where to begin, this book and in particular Ms. Buchanan’s case history, will help you out.
Mr. Sheldon will help you understand basic class organization and his unique (to the world of institutionalized education) approach to grading. By setting up coursework as a series of group and individual challenges and by creating a point system where students start with “0” and have to climb up through the levels towards their final grades, he manages (albeit not without a lot of tweaking) to make a grading system that mimics that of game progression.
In addition to just renaming groups as guilds and assignment as quests, both these teachers managed to make use of narrative to envelope the course and allowed learners considerable choice and flexibility. Narrative pulls the players/learners forward, making the course a story–their story; it creates in learners the desire to achieve hero goals; and it keeps everyone looking forward to what will happen next (Dansky, 2007). For this to work, however, there must be challenging but achievable things to do. Adoption of an inquiry-based curriculum that provides both variety and flexibility and lets the learners put their creativity to work seems a prerequisite. The balance, however, of choice and rigorous requirements seems to be a tricky one to manage (Whitton, 2012).
And even if you get that right, you’ll need to spend some time designing to facilitate greater interaction. Though it is often touted as a great feature of online games, the forming of groups to combine strengths to overcome particularly difficult challenges is not as common as game proponents might suggest. Ducheneaut (2006) studied World of Warcraft and found that players only begin to start grouping at the latter stages of game play at higher levels of the game, after they have found what they cannot do alone. That means that you can’t expect learners to collaborate on their own; you’ll have to design your activities so that group sharing is facilitated. Mr. Sheldon, for example, required both individual and group assignments during his courses, a practical way of ensuring both accountability and collaboration.
But finally, even if you get everything right, you still might not make everyone happy. There is considerable research that suggests that not all students like to experience courses as games, especially as one of those role-playing types of games that can can sound so hokey to the non-fan (Bekebrede et al., 2011).
Well, there you go. It’s obviously a challenge. It’ll take a lot of time to design all the quests and restructure the flow of lessons. But reading the stories of teachers who have done it can help you see the attraction of going whole hog with turning your course into a game. If you think you might like a little help with creating the structure and rule details, there is now a web service to help you. Called World of Classcraft, it provides roles, progressions, and rules of acquiring experience points or taking damage hit points.
And finally, you can read about an attempt to turn a language course into a large-scale alternate reality game (ARG) in Europe in Connolly, Stansfield, and Hainey (2011) linked below.
June 2013 Update: I recently came across a blog post from a teacher who had tried to gamify her class (as in turn the classroom experience into something closer to that of a game). Titled How I Turned My Classroom into a ‘Living Video Game’ and Saw Achievement Soar, the post explains (frustratingly) briefly how Ms Joli Barker, a second year elementary school teacher used technology (Skype, QR codes, GoAnimate, Voki, and Xtranormal), project-based learning narratives (?), and some international exchanges to boost the scores of her students quite dramatically. She created a basic structure of tasks and levels, challenges, and avatars, and re-tooled her assessment in a way that matches video games (similar to Mr. Sheldon). Without a little more detail, it is hard to picture what classes were really like, but the idea is very interesting and the results impressive.
Another June, 2013 update: Here is a geography class taught as a zombie survival game.
Bekebede, G., Warmelink, H., and Mayer, I. (2011). Reviewing the need for gaming in education to accommodate the net generation. Computers & Education, 57/2, 1521-1529.
Connolly, T. M., Stansfield, M., & Hainey, T. (2011). An alternate reality game for language learning: ARGuing for multilingual motivation. Computers & Education, 57(1), 1389-1415. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.01.009
Dansky, R. (2007). Introduction to game narrative. In C.M. Bateman (ed.) Game writing: Narrative skills for video games. Boston, MA: Charles River Media.
Whitton, N. (2012). Good game design is good learning design. In N. Whitton and A. Moseley (eds.) Using games to enhance learning and teaching. New York: Routledge.
Also in this EFL gamification series:
Part 1: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Rewards
Part 2: Triggers, Ability, and Motivation
Part 4: The Downside and How to Avoid It
EFL Gamification 4: The Downside and How to Avoid It
Not everyone is enamoured with gamification. Jane McGonigal wrote an entire book about using games as a force for good and avoided the term completely. And if you google “problems with gamification” you’ll come across many pages encouraging caution or vitriol against gamification. And a lot of that is from some very smart people. Stephanie Morgan, a game designer like Ms McGonigal, actually called her Nov. 2012 presentation Gamification Sucks. She says what a lot of critics say: most commercial application of gamification is based on a “shallow and cursory” understanding of the concept. Her talk covers scores and points, achievements such as badges, and avatars, and if you have 30 minutes, it is both entertaining and enlightening. Points (and other components) have to mean something, she says. That’s the whole point. That’s the whole reason we might want to use gamification in the first place.
A very nice example of this can be found at the website Progress Wars. Please go there now and click until you get it. You’ll see. Go on then. This website makes very effective use of gamification techniques to make the effective point that it can be pointedly pointless (in a bad way).
Sebastian Deterding is one of the smart people I mentioned in the first paragraph. He has a couple of presentations online that address this issue. I’ll embed them below. The first one explains the problem with most gamification really well–how it is often misunderstood and how it can often have negative side-effects. The second one looks at the same problem from a user experience design perspective and gives some suggestions for avoiding pitfalls and making experiences more playful or gameful.
For teachers, the essential problem comes down to two things, I believe. The first is that there exists already a system in place at schools for delivering content and assessing mastery. If you try to add gamification to this system, there is a strong possibility that you will be seen as just sugarcoating, in which case you can cheapen your curriculum or quickly bore your learners. The second problem is that games by definition require voluntary participation. I touched on this in the last post, but this is really the big challenge for the teacher-designer. This needs to be addressed in several ways.
One is to understand the power of the feeling of self-efficacy. Learning and progress are fun. Put another way, “kicking ass is more fun.” But there must be real achievement.
“The more we analyze and reverse-engineer passion, the more we see learning and growth as a key component. No, not a key–the key. The more knowledge and skill someone has, the more passionate they become, and the more passionate they become, the more they try to improve their knowledge and skills” (Kathy Sierra).
No teacher would disagree with this. And yet many teachers fail to help learners see evidence of achievement. Without clear goals and generous feedback–from peers, from the teacher, from the learning system–learners cannot see improvement. And if they can’t see improvement then they can’t feel improvement, and motivation will not be sustained. It’s as simple as that. Games provide fantastic feedback and teachers must get used to making something like that part of the experience in the classroom. That means clear goals and regular formative feedback and meaningful markers of progress. Yet at the same time, there must be ample opportunities to try out new skills and knowledge in low-pressure (i.e., not tested) situations. A culture of trial and error until we see progress should be cultivated. Learners will put up with a certain amount of skill-building or knowledge collection if they see how it will help get them to their goals.
But while the key component is perceived growth, something has to happen to make growth happen. Revolutions don’t start when discontents reach thresholds of self-efficacy. Revolutions use the power and passion of ideas to bring people to the barricades, people who then build the skills they need. And that takes emotion. There needs to be more emotion, more delight, more meaning involved with moving through the material. My biggest shock from observing dozens of EFL classes in Japan was the total disregard for the emotional content of the textbooks. The teachers might as well have been teaching with phone books. Now, I have many problems with the EFL textbooks in use here, but the quality of the stories used is not one of them. These stories and the characters in them can be mined for empathetic meaning. But that is not all. The course itself becomes a narrative (as I covered in the Part 3). The learners are the heroes. The design of the syllabus, the importance of the goal, the journey, and the group–all of these can contribute to the emotional content of a learning experience. Emotional engagement must be there. So the key to teaching is to take neutral learners and make them care and work enough to see themselves grow in power. And then keep this going as long as possible with further challenges, further success, and further social support. But if that were easy, it would certainly be more common than it is now. The problem is the boring bits. And maybe games can give us some ides for how to do this better.
Games are not always non-stop action. Resource farming is a common feature of games. You undertake some sort of mostly mindless repetitive activity with the knowledge that you are growing or acquiring resources/skills/information that will help you ramp up, level up, or otherwise become more powerful in the future. Take a look at Plants vs. Zombie’s zen garden.
You just collect plants, starting with only one or two, very slowly adding more. And then you water, fertilize, and provide other care for them. You water one and the others want water. You have to repeat the process. Then you have to fertilize some. Then more. Then you have to go and buy more fertilizer and do it again. The plants generate money, but your first few little plants bring in so little that you wonder whether it is worth the effort. It’s very, very close to a production line job or one of those busywork assignments some teachers are so fond of. It’s boring but the plants are cute, and in the beginning you go along with it as you try to suss out the purpose. The plants generate money, you learn, but you have to collect it, which also takes up some of your time. Eventually, however, they start generating real money and you learn that you can use that money to buy cool new super plants or unlock certain special games. So eventually you learn that this busywork contributes to a better game experience–better performance at higher levels. But there is a hump that needs to be overcome. The same is true of a lot of EFL content, particularly vocabulary. To kick ass you need to know a lot of it. But it takes time to explore the elaboration of word information, and it takes time to perform the frequent rehearsals that acquisition requires (Laufer, 2009).. And I think students will come over that hump with you if they can see the purpose in it, if they can see how their power increases.
At first glance, it seems strange that the game contains anything as slow as the zen garden. Think about it: the game shamelessly includes a an activity that at first disengages you from the main play and then forces you to complete a series of tasks that are about as fun as washing windows, despite the humorous narrator and cute little plants. And it does this on purpose! I think it’s because the designers know that players won’t respect leveling up unless it comes with some skill improvement or some work. And the same is true of learners. They’ll accept the boring bits if they promise of rewards is real. But they’ll need some help–a clear goal, very, very clear feedback, a dash of emotion, and splash of fun.
Laufer, B. (2009). Second language vocabulary acquisition from language input and from form-focused activities. Language Teaching, Vol. 42, Issue 03, July, pg. 341-254.
Also in this EFL gamification series:
Part 1: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Rewards
Part 2: Triggers, Ability, and Motivation
EFL Gamification 2: Triggers, Ability, and Motivation.
Gamification is a buzzword. Gamification is being widely–and often mistakenly–deployed in business situations recently. But because of the haphazard way it is being deployed and the mixed results it seems to be achieving, it is often viewed suspiciously by many in the world of business, and most in the world of education, where the very mention of games seems to suggest an offensive lack of seriousness. There are good and bad reasons to be suspicious of gamification, and it is not surprising that many game designers have hesitations about it.
The main problem, as I see it, is that superficial features of gamification (especially points, badges, and leaderboards) are being applied without enough thought being given to the underlying cognitive and emotional constructs people –customers, employees, learners–bring to any situation. For education, gamification, game design, and user experience (UX) design present an opportunity to re-examine the mechanics and dynamics of motivation and behavior change. Yes, they apply to teaching, including language teaching.
The first post in this series looked at intrinsic and extrinsic motivation and rewards. My main point was that depending on the type of task or behavior, the use of extrinsic rewards–like many of the the tools of gamification–can help or hinder the development of intrinsic motivation. This is a critical point, but motivation is not the only factor in behavior change. So this post will focus on behavior change and the other factors involved: triggers, ability, and context. Yes, we are still in theoretical territory here, I’m afraid. But I promise to get more practical in future posts.
B.J. Fogg, a professor at Stanford U., is someone you might not have ever heard of if you are an EFL/ESL educator. He does not do research on motivation in education. Instead, his research is in how technology changes human behavior. And his main audience is business people involved in Internet-related start-ups, trying to get people to give their ideas or services a try. EFL teachers are often faced with a challenge that is really not so different from these young entrepreneurs: how do we get learners to engage in specific behaviors, in our case, ones that we know will help them improve in proficiency? High school students in Japan are limited in the number of classroom hours of English. They are limited by a lack of technology infrastructure in schools. They are limited by the priorities of schools that want more kids to pass certain university entrance exams. That means that a lot of lesson time is spent on teacher explanations of language that is too difficult for many learners in the room, and not enough level-appropriate input is given, and not enough meaning-focused output activities are attempted. One of the possible answers to this problem is in everyone’s hands–mobile devices. But learners have no idea of how to make use of them and teachers are really really reluctant to even try to get learners to do so, fearing accusations of unfairness, steep digital learning literacy curves, and chasms of technology coordination and control issues. And the whole undertaking would require a massive shift in educational culture to begin with. But, ah, if only it were possible…Teachers could flip lessons, focus more on engaging learners in tasks requiring language production, and concentrate much much more on giving good formative feedback on comprehension or skill development in class before the final summative tests. What I would like to suggest is that by making use of better design–and that almost certainly includes some game design techniques, but will also likely include user user experience (UX) design knowledge–we can increase engagement, push learners toward being more active participants in language learning, create a better learning experience, and hopefully get increased time on task and increased effort, and (eventually) increased target language encounters outside of class. Seriously, who wouldn’t want their classes to be more fun and more effective at the same time?
But before we get into the specifics of how gamification might be able to help with behavior change, we need to look at what Mr. Fogg has to say about changing behavior. There are, of course, other researchers working on habit and behavior change. But I think Mr. Fogg has the easiest to understand and most usable of ideas. As an introduction, let’s listen to the man himself summarizing his work: a short video is available on this page (sorry, the video is not embeddable into this blog).
Mr. Fogg sees behavior change as habit formation. His lab has produced a wonderful chart that lists the different types of change by whether it involves starting a new behavior, stopping a current behavior, or increasing/reducing a current behavior. He also distinguishes the duration of the behavior change, whether it is to be temporary (dot), for a fixed period (span), or lasting (path). For language teachers in Japan dealing with low-proficiency learners (in general, students at ‘lower-level’ schools tend to have poor study skills in addition to poor language proficiency), green span or green path behaviors are what we should be aiming at. Duh, you might say at this point. But wait, because the simplistic beauty of Mr. Fogg’s model starts now. For a behavior to change, 3 things have to be present: a trigger, the ability to do the behavior, and motivation. And the last two, motivation and ability, are trade-offs. That means if you have low amounts of ability, you need to have more motivation. If you have low amounts of motivation (which is usually the case for the learners in our target group), you need to make the behavior steps really small. According to Mr. Fogg, behaviors are always the result of sequences. But you need to think and plan them carefully to be sure they meet certain conditions. That is, you need to have an appropriate trigger while you target a doable behavior with sufficient motivation available. Here is another graph that visually represents this.
First, think carefully about the target behavior. Is it simple/easy enough? Do you have a trigger? Because you need one. In the classroom, triggers can be certain events. Set fixed activities in your routines that will act as triggers. One teacher I know has his students get out their dictionaries at the beginning of class for an activity that requires them. Like clockwork, the class starts and the students get out their dictionaries as the teacher writes the day’s three vocabulary items on the board. Target behavior: use dictionaries. Trigger: vocab activity at beginning of every class. Ability: getting out the dictionaries and looking up only three words is doable. Motivation: the students want to improve at English and the teacher has convinced them that using dictionaries is important.
Think about the current motivation your learners have. Is the behavior in sync with the learners’ goals? If not, you’ll need smaller steps, like in the dictionary example above. Target behaviors in small steps (Mr. Fogg calls them tiny habits). You really can’t go wrong making your steps really really small. Once one is established, you can target a subsequent behavior. An established behavior can be used as a trigger for another behavior. You can also go the other way and work on the motivation. Explain to learners why a behavior is important. Make the activity more desirable. Or make the behavior more attractive (fun, social, meaningful, etc.). But Mr. Fogg suggests focusing on ability and triggers. Keep in mind that although people will rarely do things they don’t like, it is sometimes the case that people come to like what they do, rather than do only the things they like.
Or leverage a context change. Changes of context are times when humans are more willing and able to lose existing habits or form new ones. So, plan your big changes from the beginning of the school year. Or if you are looking to establish some new behavior, such as pair or group work, reconfigure the classroom seating and move the desks.
Here is Mr. Fogg’s list of patterns for success. These points are well worth keeping in mind as you try to get learners to change behaviors.
“Help people do what they already want to do.”
“Put hot triggers in the path of motivated people.”
“Trigger the right sequence of baby steps.”
“Simple. Social. Fun.” (You must have at least two of these.)
“Harness the motivation wave to make future behavior easy.
“Simplicity matters more than motivation.”
Another presentation of his looks at common pitfalls of behavior change. I’ll embed it below for easier access.
Now that we have covered the theoretical ground, it’s time to look at the actual application of gamification mechanics. That will be the topic of the next post.
Also in this EFL gamification series:
Part 1: Intrinsic and Extrinsic Rewards
Part 4: The Downside and How to Avoid It